As 2022 has ended and we look into 2023, it’s crucial for businesses to stay informed about the latest cyber threats.
With the increased reliance on technology and the internet in today’s business world, it’s more important than ever to be aware of potential dangers and take steps to protect your company.
Did you know that although small businesses are the target of 43% of cyber-attacks, only 14% of them are prepared to defend themselves from such cybercrime? It may sound unbelievable, but the following statistics speak for themselves —
In a 2022 case study covering the US, Canada, UK, Australia and New Zealand, 76% of respondents say their organization has suffered at least one cyberattack this year. And as if this wasn’t enough to illustrate the gravity of the situation, this is an increase of 21% since 2020!
Having that in mind, let’s take a closer look at some of the biggest cyber threats for 2022, explore what these threats mean for businesses in 2023 and what steps you can take to safeguard your company against them.
Whether you’re a small business owner or a member of a large corporation, we’ve designed this post to help you stay informed and take proactive measures to protect your business from cybercrime.
Passwords have grown even more insecure in 2022
Having been introduced in 1960 at MIT, passwords turned 62 years old in 2022. How many pieces of tech from the 1960s are you still using? Uh, yeah.
This is also reflected in the consumer attitudes towards passwords.
In fact, 68% believe passwords to be the least secure method of security while 94% are willing to take extra security measures to prove their identity. With stats like those, it’s no wonder that passwordless authentication has gained a significant foothold globally and will continue to do so.
And if you’re wondering how we got here, just take a look at the graphic below detailing the time it takes to hack different types of passwords in 2022.
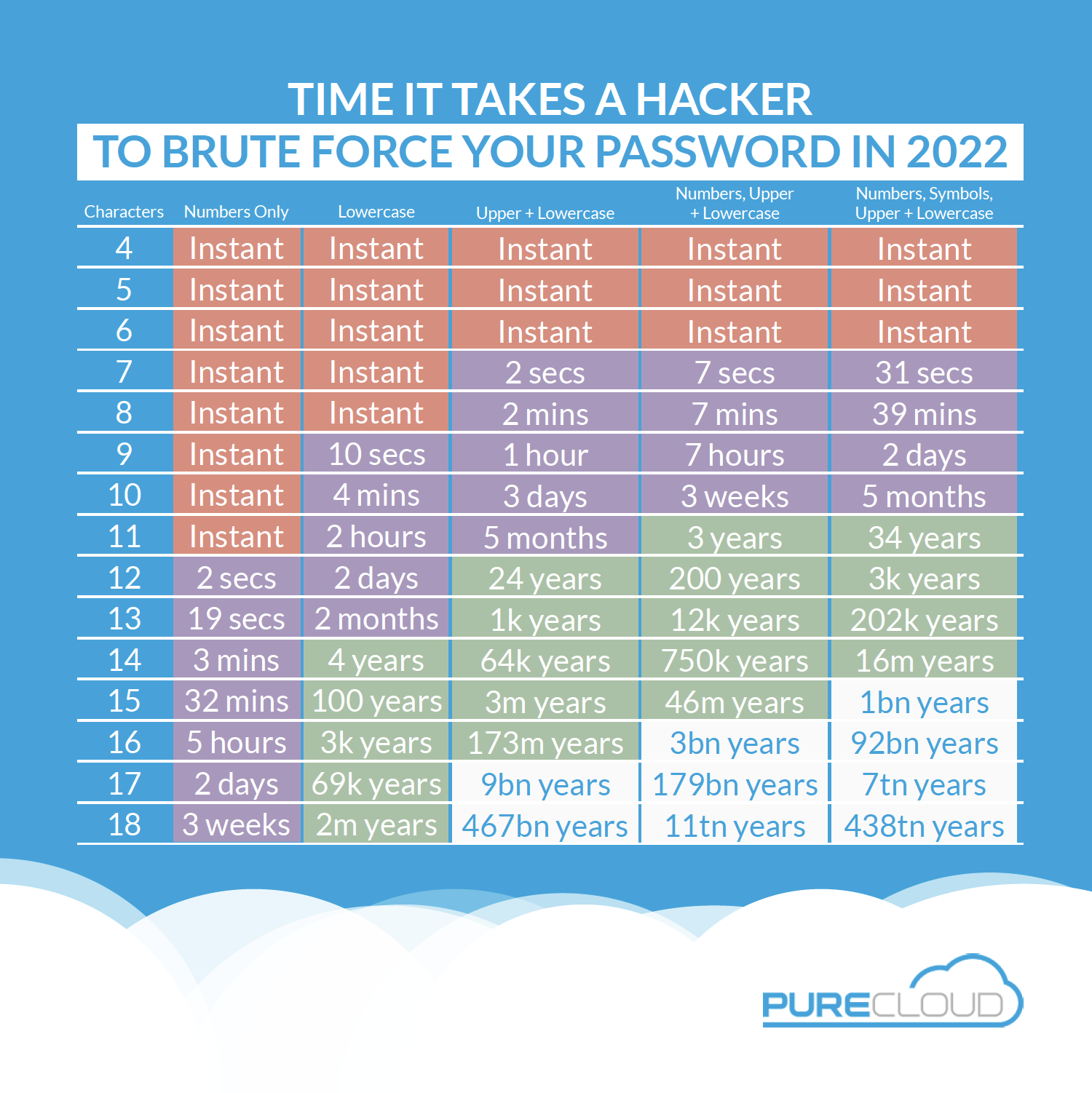
Source: purecloudsolutions.co.uk
With that in mind, if you’re not already using a password manager to create and store your passwords, we urge you to do so — as well as turn on any additional authentication factors available.
Deteriorated user trust
Did you know that 86% of people say they’re either very or somewhat concerned about the misuse of their personal information by businesses? Moreover, 58% of adults are more worried than ever of being a victim of cybercrime.
These numbers only prove a bold statement: user trust has significantly deteriorated in the light of ever-increasing cyber attacks.
In the following years, the true winners will be companies who manage to win over user trust. And there is no better way of doing this than to highlight the pillars that support your cybersecurity strategy: frictionless user experience, bank-grade security and compliance with laws and regulations.
Believing that trust is the foundation of the entire structure, this is also how we have designed IPification mobile authentication, user/transaction verification, and fraud prevention solutions.
Globally standardized, these solutions natively ensure and deliver bank-grade security, a seamless user experience, data privacy and compliance (and we’re always ready to serve and support our partners in these matters).
Companies that can effectively balance these pillars will be better positioned to earn and maintain the trust of their customers.
SIM swapping isn’t slowing down
We have covered SIM swapping on a number of different occasions. However, this fraud strategy isn’t anywhere near slowing down.
Lawsuits against cryptocurrency exchanges, digital wallet providers, and mobile network operators following cyberattacks reached a new high in 2022 — putting many of these companies at risk. Moreover, over a half of these lawsuits in Bloomberg Law’s analysis were filed against mobile network operators claiming they were responsible for the SIM swap attacks.
But the thing is: SIM swapping attempts are successful 80% of the time.
In case you haven’t yet heard about SIM swapping attacks, in this scenario, a perpetrator usually obtains a user’s personal information such as first and last name, social security number, ID numbers, etc, which they then use to trick the mobile network operator into reissuing the phone number onto a new SIM card.
Once this SIM card is active, fraudsters take advantage of all online accounts, usually financial, by taking control of SMS OTPs to verify the transactions.
That’s right! In this case, 2FA based on SMS OTP actually becomes an additional vulnerability, and especially considering the very limited number of mobile network-based authentication solutions that can prevent and detect SIM swapping in real time.
That’s why we have decided to offer IPification SIM Swap detection both as a standalone product and as part of the full package of IPification solutions. How it works is it interrupts the authentication process or sends a real-time notification to the mobile app developer when the user changes their SIM card, an essential step in preventing account takeovers. Only when this change is approved by the user is the transaction allowed to proceed.
A privacy-first approach is trending
As the number of privacy laws and regulations increase, companies are under more pressure to protect personal data. This shift towards privacy-first compliance can be seen in the way that businesses and governments are now making decisions and investments in their information security strategies.
In the past, the focus was primarily on securing information and protecting against data breaches, but now the focus is on ensuring that personal data is handled in a way that complies with privacy laws and regulations.
The digital platforms that collect and store large amounts of user data are also responding to this shift. For example, Google’s decision to end the use of third-party cookies and move to a privacy sandbox is a major step towards respecting users’ privacy. Similarly, Apple’s introduction of privacy protection features in iOS 14.5 shows a commitment to giving users more control over their data.
In the coming years, we can expect to see more companies adopt similar privacy-first approaches, either out of compliance requirements or to build trust with customers. Additionally, it’s expected that privacy legislation will continue to evolve and become even stricter, further driving the shift towards a privacy-first approach to compliance.
It will be of great importance for companies to prepare for this by implementing solutions that comply with these legislations.
It’s why we have designed IPification in a way that it doesn’t actually transfer, collect or store any personally identifiable information. Instead, it verifies the user’s identity against their unique Mobile ID key made up of the data the mobile network operator already possesses.
From buzzword to implementation: MFA and Zero Trust
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) or Zero Trust anyone? If you’re in this industry, you have to have heard about these buzzwords! But the good news is: these two concepts are increasingly being implemented into mobile apps around the world.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is important because it adds an additional layer of security to the authentication process. With MFA, a user is required to provide more than one piece of evidence to verify their identity.
This makes it more difficult for attackers to gain access to a user’s accounts or devices, as they would need to obtain multiple pieces of information rather than just a single password. In fact, according to Microsoft, MFA prevents 99.9% of cyberattacks.
On the other hand, Zero trust is an approach to security that assumes that all users and devices, both inside and outside of a company’s network, are potential threats.
This means that every access request is treated as if it is coming from an untrusted source, and appropriate measures are taken to verify the identity of the user and the security of the device before granting access.
It’s important to note that these two concepts aren’t in confrontation. As a matter of fact, together, they are just about the most powerful cybersecurity system you could adopt.
Having said that, not all implementations are the same.
As an example, MFA could protect you from phishing. But it’s important that authentication methods in your MFA system are phishing-resistant, as well. Remember that your security is only as secure as your weakest link!
And then there is the question of user experience. If it’s too tedious, the users are likely to try and find shortcuts thus defeating its purpose. That’s where a balance between security and UX comes into play.
If implemented wisely, the authentication methods in the system can verify users seamlessly while also providing security.
Let’s say you chose a combination of biometrics and IPification. Both of these methods authenticate users within milliseconds yet provide super high security. And they’re phishing resistant!
That being said, the exact implementation of the system in each app will differ based on the specific use case.
But we can help with this — as well as any other preparations for 2023 from this list. Contact us and schedule a free consultation with our cybersecurity experts. Let’s sort this out together!



